basebackup
一、pg_basebackup¶
1. 备份原理¶
pg_basebackup工具自动执行pg_start_backup()和pg_stop_backup()函数,而且备份速度比手动备份更快。
1. 备份前提¶
数据库处于归档模式
2. 备份方式¶
- 产生压缩的tar包:
pg_basebackup -D backup.tar -Ft -z -P - 产生与源文件一样的格式:
pg_basebackup -D backup -Fp -P,此备份方式块,但是不节省空间
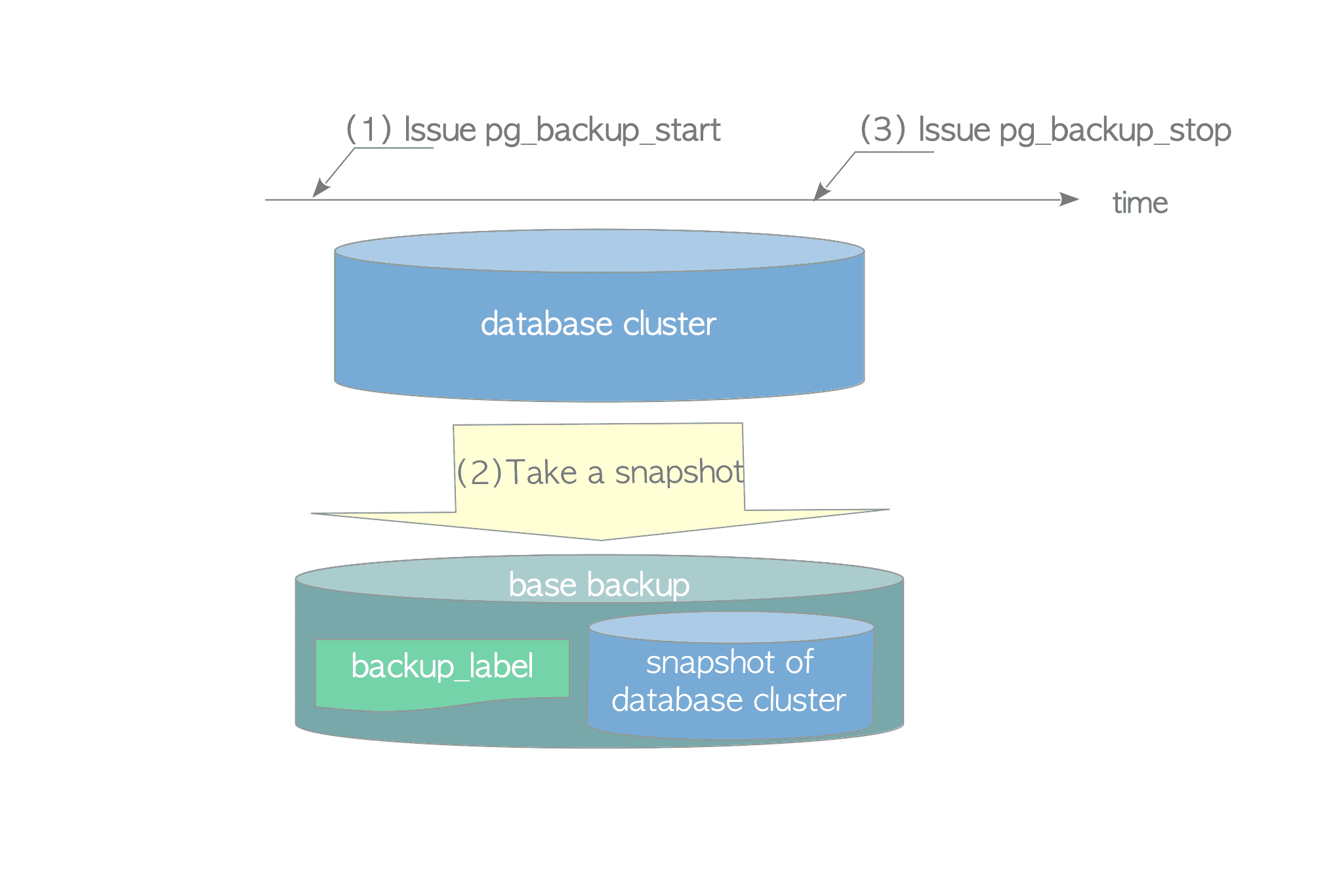
3. 备份过程¶
-
Issue the pg_start_backup command
-
Force into the full-page write mode
-
Switch to the current WAL segment file
-
Do checkpoint
-
Creat a backup_label file
backup_label与base目录同级,包含备份的基本信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
CHECKPOINT LOCATION – 记录创建的检查点的LSN位置 START WAL LOCATION – 与流复制一起使用,处于复制模式的备服务器在初始启动时读取一次该值 BACKUP METHOD – 基础备份的方法,值为'pg_start_backup'或'pg_basebackup' BACKUP FROM – 显示此备份是从主备份的还是从备备份的 START TIME – pg_start_backup执行时的时间戳 LABEL – pg_start_backup时指定的标签. START TIMELINE – 备份开始的时间线,在pg11中引入,用来进行健全性检查.
-
-
Take a snapshot of the database cluster with the archiving command you want to use
-
Issue the pg_stop_backup command
- Reset to non-full-page writes mode if it has been forcibly changed by the pg_start_backup.
- Write a XLOG record of backup end.
- Switch the WAL segment file.
- Create a backup history file – This file contains the contents of the backup_label file and the timestamp that the pg_stop_backup has been executed.
- Delete the backup_label file – The backup_label file is required for recovery from the base backup and once copied, it is not necessary in the original database cluster.
2. 用pg_start_backup()和pg_stop_backup()备份¶
确认开启归档
1 2 3 4 | |
调用pg_start_backup()开始备份
1 2 3 4 5 | |
此时$PGDATA目录下生成一个backup_label文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
调用pg_stop_backup()结束备份
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
此时,backup_label文件被删除
1 2 | |
在$PGDATA/pg_wal/新生成一个*.backup的文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
wal日志归档在/home/postgres/archive目录下
1 2 3 | |
3. 用pg_basebackup备份¶
1 2 3 4 5 | |
4. 恢复数据库¶
停止数据库
1 2 3 | |
删除$DATA/下数据
1 | |
创建空的recovery.signal文件,告诉数据库需要recovery
1 | |
恢复数据
1 2 | |
启动数据库
1 2 3 | |
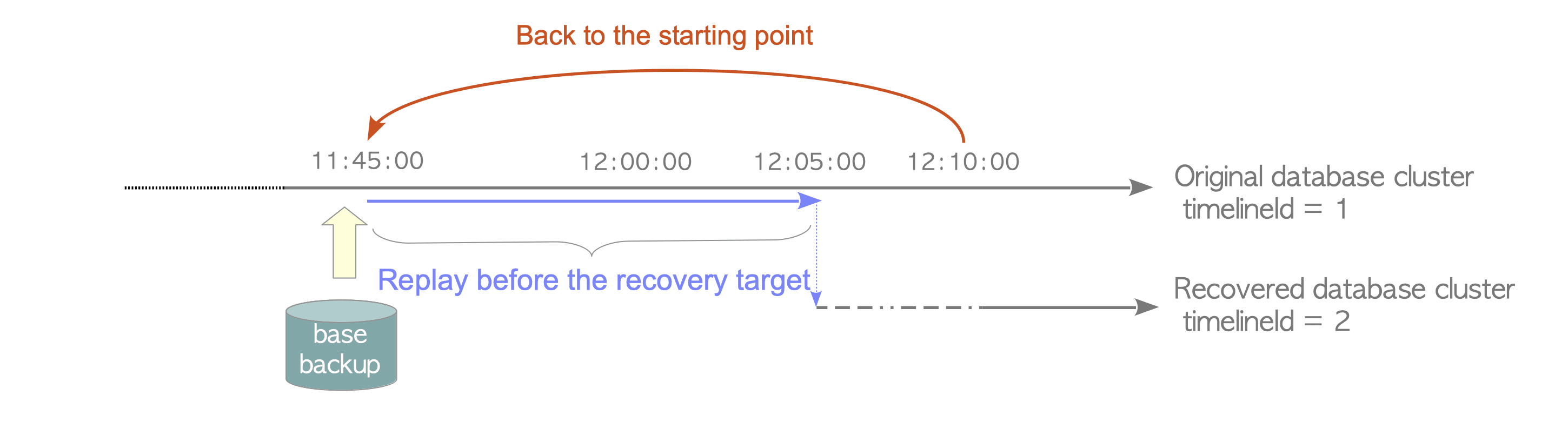
5. 时间线¶
时间线用于区分原始数据库和恢复生成的数据库。
5.1 timelineid¶
每一个时间线都会有一个相应的timelineid,每个数据库集簇都会被指定一个时间线标识。由initdb命令创建的原始数据库,其时间线标识为1。每当数据库集簇恢复时,时间线标识都会增加1。例如,在上面的例子中,从原始备份中恢复得到的数据库,其时间线标识为2。
5.2 histroy¶
恢复完成后,在生成timeline为00000002的历史文件
1 2 3 4 | |
历史文件包含了三部分:
- timelineId – timelineId of the archive logs used to recover.
- LSN – LSN location where the WAL segment switches happened.
- reason – human-readable explanation of why the timeline was changed.
recovery_target = 'immediate':指定恢复应该在达到一个一致性状态后尽快结束,在从一个在线备份恢复时,这意味着备份结束的那个点。